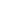
Atomic Number: 30 Period Number: 4 Group Number: 12
Zinc, which is bluish-white metal, ranks the 24th abundant element in the earth's crust. The main sources of zinc ores are sphalerite. There are five stable isotopes of Zinc in nature: 64Zn, 66Zn, 67Zn, 68Zn, 70Zn.
Zinc is mostly used as an anti-corrosive agent in other metal products. It is used in the process of galvanization. Galvanization is the coating of other metals with iron or steel, which zinc is used in, is what 50% of the worlds zinc is used for. Galvanization is used on chain-link fencing, guard rails, suspension bridges, light posts, metal roofs, heat exchangers, and car bodies. Zinc is also used as an anode on other metals particularly metals that are used in electrical works or come in contact with seawater.
Zinc Oxide ( ZnO ) is a very important zinc compound, which is white powder and insoluble in water. It is used to make plastics, ceramics, glass, pigments, food additive etc. Zinc Chloride ( ZnCl2 ) is used on lumber as a fire retardant and preserver.
Physical and Chemical properties:
Atomic Weight: 65.38
Melting Point: 692.68 K
Boiling Point: 1180 K
Density: 7.134 g/cm3
Phase at Room Temperature: Solid
Ionization Energy: 9.394 eV
Oxidation State: +2
See also:
Wikipedia - Basics on Zinc
WebElements - The basic elements of Zinc
Jefferson Lab - Learning about Zinc