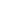
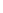
Atomic Number: 5 Period Number: 2 Group Number:13
Boron compounds were known for thousands of years ago, but the pure boron was produced until 1808 by two French chemists. It exists in nature mainly by borate minerals. Heating borax with carbon is the key process to obtain boron.
Boron is used in pyrotechnics and flares to produce a green color and also used in some rockets.
Boron compounds play an important role in making glass, ceramics, bleach, semiconductors and magnets. There are two important compounds of Boron - Boric Acid (H3BO3) and Sodium tetraborate pentahydrate (Na2B4O7·5H2O). Most of sodium tetraborate pentahydrate are used in the manufacture of fiberglass insulation and bleach.
Physical and Chemical properties:
Atomic Weight: 10.811
Melting Point: 2348 K
Boiling Point: 4273 K
Density: 2.37 g/cm3
Phase at Room Temperature: Solid
Element Classification: Semi-metal
Ionization Energy: 8.298 eV
Oxidation State: +3
See also:
Wikipedia - Basics on Boron
WebElements - The basic elements of Boron
Jefferson Lab - Learning about Boron