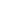
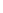
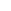
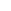Atomic Number: 20 Period Number: 4 Group Number: 2
Calcium is the fifth most abundant element in the earth's crust, which is very unstable and can be reacted with water and oxygen easily. So it always exits in nature as compound. Ca2+ is an essential elements for living organisms and it is a major material used to form our shells, bone and teeth.
Metallic calcium is used for refining other metals, such as zirconium, and also some of them will be made as calcium alloy, but the demand limits.
There are many kinds of calcium compounds, such as calcium carbonate (CaCO3), calcium sulfate( CaSO4) and calcium nitrate [Ca(NO3)2]. Calcium carbonate is the basis of the cement industry, either as a building material or limestone aggregate for roadbuilding or as an ingredient of cement or as the starting material for the preparation of builder's lime by burning in a kiln.
Physical and chemical properties:
Atomic Weight: 40.078
Melting Point: 1115 K
Boiling Point: 1757 K
Density: 1.54 g/cm3
Phase at Room Temperature: Solid
Ionization Energy: 6.113 eV
Oxidation State: +2
See also:
Wikipedia - Basics on Calcium
WebElements - The basic elements of Calcium
Jefferson Lab - Learning about Calcium